Modern enterprises are standardizing on transparent, inspectable AI foundations to manage risk, scale innovation, and maintain control. As AI adoption accelerates, open source AI is emerging as the most reliable base for secure, auditable, and enterprise-grade workloads across cloud, data, and security domains.
Enterprises did not arrive here by ideology. They arrived here by necessity. The rise of generative systems introduced new attack surfaces, misuse risks, and dependency lock-ins that traditional proprietary models could not fully address. Decision-makers now prioritize traceability, governance, and ecosystem resilience over novelty.
This shift is redefining how organizations think about AI platforms, tooling, and long-term architecture. Open ecosystems, shared intelligence, and defensible controls are becoming core enterprise requirements, not optional enhancements.
1. The Enterprise Reframing of Open Source AI
Open source AI has moved decisively out of the developer experimentation phase and into the executive decision stack. What was once evaluated for flexibility and cost efficiency is now assessed as a strategic control layer for enterprise AI operations. Boards, CISOs, and CTOs increasingly view open source AI meaning as infrastructure that enables trust, governance, and long-term resilience.
This reframing is driven by reality, not ideology. As AI systems influence revenue, compliance, security posture, and brand risk, enterprises must understand how these systems behave under normal conditions and under stress. Open source AI offers the level of transparency and adaptability required to manage those outcomes responsibly.
From Innovation Speed to Risk Control
Early AI adoption cycles rewarded speed above all else. Teams raced to deploy models, integrate APIs, and demonstrate immediate value. That phase exposed a critical gap. Fast deployment without deep visibility created blind spots in accountability, security, and misuse detection.
Today, enterprises prioritize control and assurance over raw velocity. Leaders need to know how models respond to edge cases, how they can be manipulated, and how mitigation strategies evolve as threats change. Open source software supports this shift by allowing direct inspection of model behavior, training logic, and inference pathways. This visibility turns AI from an opaque service into a governable system.
Open Source Software Meaning in an AI Context
Open source software meaning changes significantly in AI environments. It is not simply about code availability. In enterprise AI, it represents the ability to trace how a model was trained, how data flows through pipelines, and how safeguards are implemented and tested.
Inspectable training processes enable reproducibility. Reproducible pipelines enable auditing. Community-reviewed safeguards improve defensive quality. Shared defensive patterns allow enterprises to learn from each other’s failures and successes. This collective transparency in open source development is foundational for confidence at scale and critical for regulated and risk-sensitive environments.
2. Why Generative AI Accelerated the Open Shift
Generative AI introduced operational risks that traditional software controls were not designed to handle. These systems can be influenced by prompts, manipulated through indirect inputs, and exploited to generate harmful or misleading outputs at scale.
Closed AI stacks struggled to adapt quickly to these realities. Limited visibility into model internals made it difficult for enterprises to diagnose issues, simulate misuse, or implement custom defenses. This pressure accelerated the shift toward open source tools, where adaptability and shared intelligence are built into the ecosystem.
Open Source Information as a Defensive Asset
Open source information has become a defensive asset in AI operations. Enterprises use shared research, community disclosures, and collaborative testing to identify emerging misuse patterns and refine controls continuously.
This mirrors the evolution of open threat intelligence in cybersecurity. Shared indicators, techniques, and mitigation strategies strengthened the entire ecosystem of open source benefits. In AI, open source information plays the same role by enabling faster detection, better defenses, and informed decision-making across organizations.
3. Enterprise Governance by Open Source AI
The strongest argument for open source AI for enterprises is governance. Enterprises must be able to explain how AI decisions are made, audit outcomes, and defend those decisions to regulators, customers, and internal stakeholders.
Governance is not a bolt-on feature. It must be embedded throughout the AI lifecycle. Open source AI provides the structural access required to design governance into models, pipelines, and operational processes from the start.
Licensing Enables Predictable Control by Open Source AI
Open source licensing creates predictability. Clear rules around usage, modification, and redistribution reduce ambiguity and legal risk. For enterprises operating across regions and regulatory regimes, this clarity is essential.
Predictable licensing also supports long-term planning. Enterprises avoid sudden cost shifts, forced migrations, or restrictive usage changes. This stability of open source software is particularly important for mission-critical AI workloads that cannot tolerate disruption.
Policy Enforcement and Model Oversight
When AI model open source access is available, enterprises can implement policy enforcement directly within the model lifecycle. Security controls, monitoring hooks, and red-team simulations can be integrated at training, deployment, and inference stages.
This level of oversight is not achievable when model internals are opaque. Open access allows enterprises to test assumptions, validate safeguards, and continuously refine controls as new risks emerge.
4. Architecture Patterns Powering the Open Source AI Ecosystem
The open source AI ecosystem favors modular, composable architectures over tightly coupled platforms. This design philosophy aligns well with enterprise requirements for scalability, resilience, and change management.
Modularity of open source software allows teams to upgrade components independently, experiment safely, and respond quickly to evolving requirements without destabilizing production systems.
Core Components of Open Source AI
Typical enterprise architectures include open source models, orchestration frameworks, security filters, evaluation harnesses, and telemetry pipelines. Each component serves a specific purpose and communicates through defined interfaces.
This separation of concerns enables controlled evolution. Models can improve without rewriting governance logic. Security layers can adapt without retraining systems. Enterprises gain flexibility without sacrificing stability.
Open Source Cloud Alignment
Open source cloud environments support elastic scaling while preserving portability. Enterprises can deploy AI workloads where performance, compliance, and data residency requirements are best met.
This alignment reduces dependency risk and supports hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. Enterprises retain operational freedom while meeting performance and regulatory expectations.
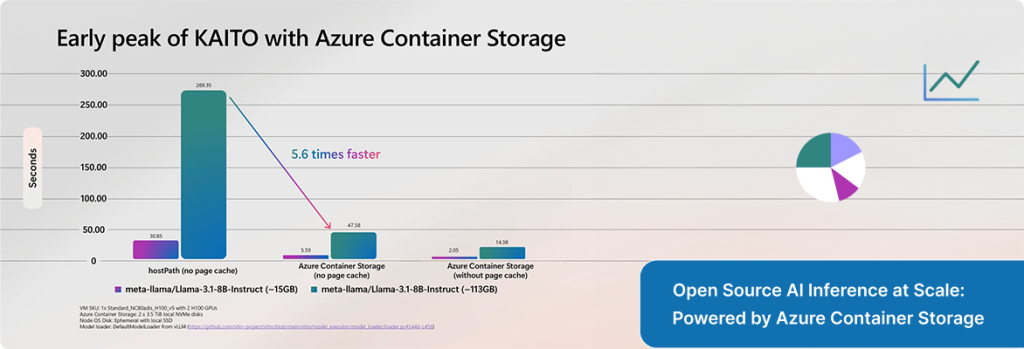 Source: Microsoft
Source: Microsoft
5. Benefits of Open Source AI Across Enterprise Systems
The benefits of open source compound over time. They are not limited to initial cost savings or development speed. They influence resilience, innovation capacity, and strategic control.
Operational Resilience of Open Source AI
Shared maintenance reduces reliance on single vendors. When vulnerabilities or failures occur, community-driven fixes often emerge faster than proprietary patches. Enterprises benefit from collective vigilance.
Faster Defensive Innovation
Threat patterns identified by one organization can be addressed by many. This network effect accelerates defensive innovation and improves overall ecosystem maturity.
Cost Transparency
Open source tools provide predictable cost structures. Enterprises invest in internal capability, infrastructure, and governance rather than opaque licensing models. This transparency supports better budgeting and long-term ROI analysis.
6. Best Practices for Enterprise Adoption of Open Source AI
Successful enterprise adoption of open source AI depends less on tooling choices and more on operating discipline. Organizations that treat adoption as an engineering exercise alone often struggle. Those that approach it as a governance and systems design problem scale with confidence.
Start with Guardrails
Enterprises should define guardrails before any model is deployed. This includes acceptable use policies, prohibited behaviors, data handling rules, and decision boundaries for automated outputs. Guardrails are not theoretical documents. They must be encoded into workflows, access controls, and monitoring systems.
Monitoring thresholds should be explicit and measurable. Teams need clarity on what constitutes abnormal behavior, misuse indicators, or output drift. Escalation paths must be predefined so incidents move quickly from detection to response. Without this structure, even well-designed open source systems become operational liabilities.
Separate Model and Policy Layers
Governance logic should never be tightly coupled to model logic. Models will evolve. Policies must evolve faster. Keeping these layers independent allows enterprises to adapt controls without retraining or redeploying core systems.
This separation enables rapid response to new threats, regulatory changes, or business requirements. Enterprises can introduce new filters, approval steps, or audit mechanisms with the help of open source software, without disrupting model performance. This design pattern is foundational for long-term maintainability and risk management.
Invest in Evaluation Pipelines
Accuracy benchmarks are insufficient for enterprise AI development service. Models must be continuously tested against misuse scenarios, adversarial prompts, and operational edge cases. Evaluation pipelines should simulate real-world abuse, not idealized usage.
These pipelines act as early warning systems. They surface weaknesses before they become incidents. Over time, enterprises build institutional knowledge about how models behave under pressure. This feedback loop strengthens both security posture and business reliability.
Limitations and Trade-Offs
Open source AI is not inherently safer or easier. It shifts responsibility from vendors to enterprises. That shift requires internal expertise, disciplined governance, and sustained operational investment.
Enterprises must maintain models, monitor behavior, and respond to emerging risks. There is no external safety net. The trade-off is clear. In exchange for transparency and control, organizations accept ownership of outcomes. For many enterprises, that responsibility is preferable to blind dependence on opaque systems.
7. Open Source AI as an Intelligence Multiplier
At Flexsin, we view open source AI as an intelligence multiplier, not a cost-saving shortcut. When treated as shared infrastructure, open ecosystems amplify defensive insight, operational resilience, and strategic flexibility.
Organizations that invest in governance, evaluation, and collaboration gain compounding benefits. Those that adopt open source AI casually inherit unmanaged risk. Our work across cloud platforms, data systems, and cyber threat intelligence consistently shows that open ecosystems outperform closed ones when adversaries adapt faster than vendors can respond.
Enterprises building AI capabilities today are also defining their future risk posture. Open source AI provides the foundation for transparent, defensible, and resilient systems at scale. It is becoming the default not because it is free, but because it is controllable.
To navigate AI misuse risks, governance design, and threat-aware architectures, engage with Flexsin’s cyber threat intelligence and AI security teams. We help enterprises operationalize open source AI with confidence, control, and measurable impact.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is open source AI trusted more by enterprises?
Trust comes from visibility. Open source AI allows enterprises to inspect model behavior, audit decisions, and validate safeguards. This transparency supports defensible decision-making at scale.
2. Is open source AI less secure than proprietary AI?
Security is a function of governance, not licensing. Open systems often surface vulnerabilities faster through community review. Without governance, both open and closed systems fail.
3. How does open source licensing affect AI deployment?
Licensing clarifies usage rights, modification permissions, and redistribution rules. This reduces legal ambiguity and supports predictable long-term deployment planning.
4. Can open source AI scale for large enterprises?
Yes. Modular architectures support horizontal scaling, distributed workloads, and multi-cloud strategies without sacrificing control or performance.
5. What role does open source information play in AI defense?
It enables shared learning. Enterprises benefit from collective insight into misuse patterns, attack techniques, and effective mitigations.
6. Are open source tools production-ready?
Many are enterprise-grade when paired with strong governance, monitoring, and operational discipline. Readiness depends on implementation, not origin.
7. How do enterprises manage misuse risks in open models?
Through layered controls. Policy enforcement, continuous evaluation, and adversarial testing work together to reduce exposure.
8. Does open source AI reduce vendor lock-in?
Yes. Portability and interoperability are core advantages, especially for long-term AI strategies.
9. Is open source AI suitable for regulated industries?
With proper governance and compliance mapping, it often exceeds the transparency and auditability of closed systems.
10. What skills are required to manage open source AI?
Enterprises need architectural thinking, security engineering, data governance expertise, and operational discipline.


 Munesh Singh
Munesh Singh